Comprehensive Guide to FX Spot Trading for Beginners: Dive headfirst into the thrilling, slightly terrifying world of foreign exchange! Think of it as a global casino, but instead of chips, you’re juggling currencies, and the house always has a slight edge (unless you’re incredibly savvy, of course). This guide will arm you with the knowledge to navigate this exhilarating market, turning potential losses into profitable wins (hopefully!).
Prepare for a wild ride!
We’ll unravel the mysteries of currency pairs, from the mighty EUR/USD to the more exotic pairings. You’ll learn to decipher the cryptic language of pips, lots, and spreads, mastering the art of reading charts like a seasoned crypto-fortune teller. We’ll equip you with the tools – trading platforms, technical indicators, and risk management strategies – to chart your course to forex success.
Get ready to conquer the currency cosmos!
Introduction to FX Spot Trading
So, you’re thinking about diving into the thrilling world of foreign exchange (FX) trading? Buckle up, buttercup, because it’s a wild ride! This guide will gently ease you into the complexities of the FX spot market, a global marketplace where currencies are bought and sold like…well, like hotcakes on a particularly good day. We’ll demystify the jargon, explore the history, and equip you with the basic knowledge to navigate this exciting, and potentially lucrative, arena.FX spot trading is simply the buying and selling of currencies at the current market price for immediate settlement, typically within two business days.
Think of it as a giant, global auction where everyone is trying to get the best deal on different currencies. The value of one currency relative to another fluctuates constantly based on a multitude of factors, creating both opportunities and risks. Understanding these fluctuations is key to success.
Key Terms in FX Spot Trading
Understanding the language of FX trading is crucial. Let’s break down some essential terms:A pip (point in percentage) is the smallest price movement in a currency pair. For most currency pairs, it’s 0.0001. Think of it as the smallest increment on a ruler. A small change, but these tiny movements add up!A lot refers to the standard unit of currency traded.
A standard lot is typically 100,000 units of the base currency. This might sound intimidating, but don’t worry; we’ll discuss lot sizes in more detail later. Think of it like buying shares of stock – you don’t need to buy thousands to start.The bid/ask spread is the difference between the price at which you can buy a currency (ask price) and the price at which you can sell it (bid price).
This spread is the broker’s profit margin. It’s a cost of doing business, much like a sales tax. Leverage is the ability to control a larger position with a smaller amount of capital. It acts like a magnifying glass, amplifying both profits and losses. Leverage is a double-edged sword; it can significantly increase your potential returns, but it also increases your risk.
A Brief History of the FX Market
The FX market wasn’t always the high-tech, 24/7 behemoth it is today. Its origins can be traced back centuries, with early forms of currency exchange arising from the need to facilitate international trade. The Bretton Woods Agreement in 1944 established a system of fixed exchange rates, but this system eventually collapsed in the 1970s, leading to the floating exchange rate system we have today.
The rise of electronic trading in recent decades has transformed the FX market into the largest and most liquid financial market globally, with trillions of dollars changing hands every day.
Types of FX Trading Accounts, Comprehensive guide to FX spot trading for beginners
Beginners typically have a few account options to choose from. The most common are:
- Standard Accounts: These accounts offer standard leverage and are suitable for traders who are comfortable with the risks associated with leverage.
- Mini Accounts: These accounts offer smaller lot sizes, making them ideal for beginners with limited capital. They provide a less risky way to learn the ropes.
- Micro Accounts: These accounts offer even smaller lot sizes than mini accounts, providing a very low-risk entry point for those just starting out.
The best account type for you will depend on your trading style, risk tolerance, and capital. It’s crucial to choose an account that aligns with your experience level and financial goals. Don’t jump in headfirst; start small and learn as you go.
Understanding Currency Pairs and Market Dynamics
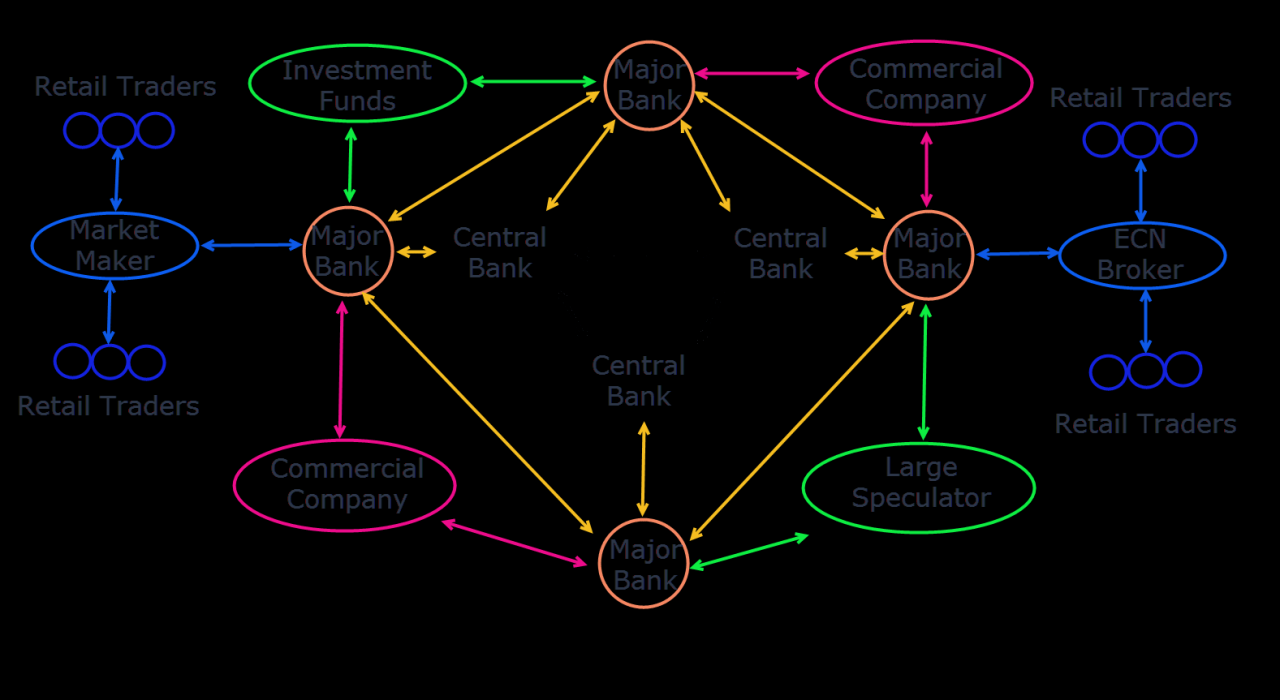
So, you’ve dipped your toe into the world of FX spot trading. Congratulations! Now, let’s navigate the thrilling, slightly chaotic, and undeniably lucrative waters of currency pairs. Think of it as a global game of musical chairs, but instead of chairs, there’s money, and instead of music, there’s economic data.Currency pairs are, as the name suggests, two currencies paired together.
For example, EUR/USD represents the Euro (EUR) against the US Dollar (USD). The first currency is called the “base currency,” and the second is the “quote currency.” A EUR/USD exchange rate of 1.10 means that 1 Euro can be exchanged for 1.10 US Dollars. Simple, right? (Well, mostly.)
Currency Pair Classifications
The FX market isn’t just a homogenous blob of currencies; it’s neatly (or perhaps messily) categorized. We have major, minor, and exotic pairs, each with its own personality quirks. Major pairs involve the US dollar against other major global currencies like the Euro (EUR/USD), British Pound (GBP/USD), Japanese Yen (USD/JPY), and the Swiss Franc (USD/CHF). These are the most liquid and heavily traded, meaning you can buy and sell them easily with minimal price slippage.
Minor pairs involve two major currencies, but without the US dollar, like EUR/GBP or EUR/JPY. These pairs tend to be slightly less liquid than the majors but still offer decent trading opportunities. Finally, exotic pairs pair a major currency with the currency of an emerging market, like USD/MXN (US Dollar/Mexican Peso) or EUR/TRY (Euro/Turkish Lira). These are less liquid and more volatile, offering potentially higher rewards but also greater risk.
Think of it as a thrilling rollercoaster ride versus a comfortable train journey.
Factors Influencing Exchange Rates
Exchange rates aren’t static; they’re constantly fluctuating based on a variety of factors, creating a dynamic and exciting market. Imagine them as highly caffeinated butterflies, fluttering unpredictably based on global news. Economic data releases (like inflation rates, GDP growth, and employment figures) significantly impact currency values. A strong economy usually boosts its currency, while a weak one leads to depreciation.
Political events, such as elections or policy changes, can also cause dramatic shifts. For example, unexpected political instability in a country can cause its currency to plummet. Global events, such as pandemics or wars, can also significantly impact exchange rates, often causing widespread volatility. Market sentiment, driven by trader psychology and speculation, plays a crucial role. Even news headlines, true or not, can influence currency movements.
Currency Pair Volatility and Liquidity
The following table provides a general comparison. Remember, these are broad generalizations, and actual volatility and liquidity can vary significantly depending on market conditions.
| Currency Pair | Volatility | Liquidity | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| EUR/USD | Medium | High | Most traded pair, relatively stable |
| GBP/USD | Medium-High | High | Significant influence from UK economic news |
| USD/JPY | Medium | High | Often used as a safe haven during times of uncertainty |
| USD/MXN | High | Medium | Highly sensitive to Mexican economic conditions and US-Mexico relations |
Trading Platforms and Tools
Stepping into the thrilling world of FX spot trading is like entering a high-tech casino, except instead of chips, you’re juggling currencies. And just like a seasoned gambler needs the right tools, you’ll need a powerful trading platform and a suite of analytical instruments to navigate this exciting, and sometimes volatile, landscape. Choosing the right platform is crucial; it’s your digital cockpit for controlling your financial flight.
Popular FX Trading Platforms and Their Features
The FX trading world offers a smorgasbord of platforms, each boasting unique features. MetaTrader 4 (MT4) and MetaTrader 5 (MT5), for example, are industry veterans known for their robust charting capabilities, extensive indicator libraries, and automated trading options (Expert Advisors or EAs). Think of them as the trusty workhorses of the FX trading world. cTrader, on the other hand, is praised for its speed and sleek, modern interface, perfect for those who appreciate a streamlined experience.
Each platform has its strengths and weaknesses, and the best choice depends on your individual trading style and preferences. Some platforms offer superior charting tools, while others excel in automated trading capabilities. Consider factors like ease of use, charting capabilities, available indicators, and the platform’s reputation for reliability and security before making your choice.
Charting Tools and Their Functionalities
Charts are your window into the forex market’s soul. They visually represent price movements over time, allowing you to identify trends, support and resistance levels, and potential trading opportunities. Different chart types—candlestick, bar, line—offer unique perspectives. Candlestick charts, for instance, visually represent the opening, closing, high, and low prices of a currency pair over a specific period, providing a rich tapestry of price action information.
Bar charts offer a similar overview, while line charts simplify the visual representation, focusing primarily on price movement. Beyond the chart type, you’ll find a plethora of drawing tools—trend lines, Fibonacci retracements, support/resistance levels—to help you analyze market behavior and formulate trading strategies. The ability to zoom in and out, change timeframes (from seconds to years), and customize the chart’s appearance is essential for effective analysis.
So you’re diving headfirst into the wild world of FX spot trading? Our comprehensive guide for beginners will help you navigate the choppy waters, but remember, even seasoned sailors need a life raft! That’s where understanding risk management comes in – check out this essential guide on Best practices for managing risk when forex trading with Questrade to avoid becoming a financial shipwreck.
Then, armed with knowledge and a healthy dose of caution, you can confidently return to mastering those FX spot trades!
Technical Indicators: Moving Averages, RSI, and MACD
Technical indicators are like the market’s crystal ball (though not perfectly accurate, of course!). They analyze historical price data to provide insights into potential future price movements. Moving averages (MAs), for instance, smooth out price fluctuations, helping to identify trends. A simple moving average (SMA) calculates the average price over a specified period, while an exponential moving average (EMA) gives more weight to recent prices.
The Relative Strength Index (RSI) measures the magnitude of recent price changes to evaluate overbought or oversold conditions, potentially signaling reversals. The Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) indicator uses moving averages to identify momentum changes and potential trend reversals. Remember, indicators are tools, not oracles. Use them in conjunction with other forms of analysis and never rely solely on a single indicator to make trading decisions.
Risk Management Tools: Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Orders
In the FX trading arena, risk management isn’t just a good idea—it’s a survival necessity. Stop-loss orders automatically exit a trade when the price moves against you by a predetermined amount, limiting potential losses. Imagine a stop-loss order as your parachute in a financial freefall. Take-profit orders, conversely, automatically close a trade when the price reaches a predetermined profit target, locking in your gains.
Think of it as setting your profit goal and letting the market do the work. These orders are crucial for protecting your capital and managing your risk exposure. Properly setting stop-loss and take-profit orders is essential for long-term success in FX trading. A well-defined risk management strategy, incorporating these orders, is crucial for navigating the inherent volatility of the market.
Developing a Trading Strategy
So, you’ve learned the basics of FX spot trading – congratulations! Now comes the fun (and slightly terrifying) part: creating a trading strategy. Think of this as your personal FX battle plan, a roadmap to navigate the sometimes chaotic world of currency markets. Without a solid strategy, you’re essentially throwing darts blindfolded – hoping for the best, but mostly accepting the worst.
A well-defined strategy provides structure, discipline, and – crucially – helps you manage risk.Choosing the right trading strategy depends on your personality, risk tolerance, and available time. There’s no one-size-fits-all approach, so let’s explore some popular options.
Trading Strategy Types
Different trading strategies cater to different trading styles and time horizons. Scalping, day trading, and swing trading are three popular approaches, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these differences is key to selecting the strategy that aligns best with your capabilities and goals.
- Scalping: This involves making many small trades throughout the day, aiming for tiny profits on each one. Think of it as picking up pennies in front of a steamroller. High volume and quick execution are essential. The potential for quick profits exists, but so does the potential for equally quick losses if things go south.
- Day Trading: Day traders open and close all positions within a single trading day. They capitalize on intraday price fluctuations, aiming for larger profits than scalpers but requiring more time and attention. Think of it as catching a few decent-sized fish instead of a lot of tiny ones. Risk management is still paramount, but the potential rewards are higher.
- Swing Trading: Swing traders hold positions for several days, or even weeks, profiting from larger price swings. This approach requires patience and a good understanding of market trends. It’s more like deep-sea fishing; you might wait longer for a catch, but it’s likely to be much bigger when you do.
Fundamental vs. Technical Analysis
The two main approaches to market analysis are fundamental and technical. They’re not mutually exclusive; many traders use a combination of both.
- Fundamental Analysis: This focuses on economic indicators, political events, and other factors that influence currency values. Think big picture – interest rates, inflation, GDP growth, geopolitical stability. For example, a surprise interest rate hike by a central bank could significantly impact the value of its currency.
- Technical Analysis: This uses charts and technical indicators to identify trends and predict future price movements. It focuses on price action, volume, and other market data, disregarding the underlying economic fundamentals. Think patterns, support and resistance levels, moving averages, and other indicators – essentially, reading the tea leaves of the market.
Sample Trading Plan
A well-structured trading plan is crucial. It Artikels your strategy, entry and exit points, risk management, and position sizing. Here’s a simple example for a day trading strategy using technical analysis:
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Trading Style | Day Trading (EUR/USD) |
| Entry Point | Buy when the 50-day moving average crosses above the 200-day moving average, with confirmation from a bullish candlestick pattern. |
| Exit Point | Sell when the price falls below a predetermined support level or when the RSI indicator reaches overbought territory (e.g., above 70). |
| Risk Management | Use a stop-loss order to limit potential losses to 1% of the trading account. |
| Position Sizing | Risk no more than 1% of your trading capital per trade. |
Executing a Trade
Executing a trade involves several steps, from placing the order to closing the position. Let’s walk through a simplified process.
- Order Placement: Use your trading platform to enter a buy or sell order, specifying the currency pair, quantity, and stop-loss and take-profit levels.
- Order Confirmation: Once the order is executed, you’ll receive confirmation from your broker.
- Monitoring the Trade: Regularly monitor the market and your open positions. Be prepared to adjust your stop-loss or take-profit levels as needed.
- Closing the Position: Close your position by placing a sell order (if you bought) or a buy order (if you sold) when your exit criteria are met or if the market moves against you significantly.
Risk Management and Money Management
Let’s face it: FX trading isn’t a get-rich-quick scheme, despite what those flashy online ads might suggest. It’s a game of skill, strategy, and – crucially – managing your risk. Ignoring risk management is like sailing a yacht without a rudder: you might have a beautiful boat, but you’ll likely end up shipwrecked. This section will equip you with the life vest and compass you need to navigate the sometimes turbulent waters of the forex market.Risk management in FX trading isn’t just about protecting your capital; it’s about ensuring you can stay in the game long enough to learn, adapt, and ultimately, profit.
Without a solid risk management plan, even the most brilliant trading strategy can quickly turn sour. Think of it as the safety net for your financial acrobatics.
Position Sizing
Position sizing determines how much of your capital you allocate to each trade. It’s about finding the sweet spot between maximizing potential profits and minimizing potential losses. A common approach is to risk only a small percentage of your account balance (e.g., 1-2%) on any single trade. For instance, if you have a $10,000 account and risk 1%, your maximum loss per trade would be $100.
This approach allows you to withstand a series of losing trades without completely wiping out your account. Overly aggressive position sizing, on the other hand, can lead to rapid account depletion, a situation known as “blowing up your account.” This is akin to betting your entire life savings on a single roulette spin – exciting, perhaps, but exceptionally unwise.
Stop-Loss Orders
Stop-loss orders are your automated safety net. They’re instructions to your broker to automatically close a trade when the price moves against you by a predetermined amount. Let’s say you buy EUR/USD at 1.1000 and set a stop-loss order at 1.0980. If the price falls to 1.0980, your trade will be automatically closed, limiting your potential loss to 20 pips (0.0020).
This prevents emotional trading decisions, like holding onto a losing trade hoping it will recover. Think of it as your automated “panic button” for your trades. It’s crucial to place stop-loss orders strategically, considering market volatility and your risk tolerance.
So you’re diving headfirst into the wild world of FX spot trading? Our comprehensive guide for beginners will get you started, but before you leap, you might want to check out Comparing Questrade’s forex offerings with other Canadian brokers to find the best platform for your needs. Then, armed with knowledge and the perfect broker, you’ll be ready to conquer the forex market!
Effective Money Management Strategies
Effective money management isn’t just about position sizing and stop-losses; it’s about a holistic approach to capital preservation and growth. A fixed fractional approach, as mentioned earlier (risking a fixed percentage of your account on each trade), is a common and effective strategy. Another approach is the Kelly Criterion, a mathematical formula that calculates the optimal bet size based on your win probability and average win/loss ratio.
However, the Kelly Criterion can be quite complex for beginners, and often leads to over-aggressive trading if improperly understood. Therefore, a simple fixed fractional approach is usually the best starting point.
Psychological Aspects of Trading and Strategies for Emotional Control
Trading can be an emotional rollercoaster. Fear, greed, and hope can cloud your judgment and lead to impulsive decisions. Successful traders cultivate emotional discipline. Techniques like keeping a trading journal to track your trades and analyze your emotions, maintaining a disciplined trading plan, and taking regular breaks from the market to avoid burnout are crucial. Remember, trading is a marathon, not a sprint.
Patience and emotional control are just as important as technical analysis and trading strategies. Consider seeking guidance from a qualified trading coach if you struggle with emotional discipline, as the financial impact of poor emotional control can be significant.
So you’ve conquered the basics with our comprehensive guide to FX spot trading for beginners? Fantastic! But ready to level up your game and ditch the guesswork? Then check out this guide on Mastering the ATS trading system for forex trading success to automate your wins (and maybe even your coffee breaks!). After mastering the ATS, you’ll be back to dominating the FX spot market like a pro!
Demo Accounts and Practice Trading
Before you unleash your inner Warren Buffett (or George Soros, if you’re feeling particularly ambitious) on the live forex market, it’s crucial to understand that a trial by fire isn’t always the best approach. Think of it like this: you wouldn’t attempt a triple backflip on a trampoline without a few practice runs, would you? Demo accounts are your virtual trampoline, allowing you to perfect your moves before risking real money.Demo accounts offer a risk-free environment to learn the ropes of forex trading.
You get to experience the thrill (and sometimes the terror) of trading without the stomach-churning fear of losing your hard-earned cash. It’s the perfect sandbox for experimenting with different strategies, testing your emotional resilience, and getting a feel for the market’s unpredictable nature. Essentially, it’s like playing a high-stakes game of simulated financial poker – all the fun, none of the debt collectors.
Benefits of Using a Demo Account
Utilizing a demo account provides numerous advantages for aspiring forex traders. It allows for risk-free experimentation with trading strategies, familiarization with trading platforms, and assessment of personal trading psychology under pressure. This practice significantly reduces the financial risk associated with live trading, allowing for a smoother transition into the real market. Think of it as your personal forex training wheels – you can pedal away to your heart’s content without the worry of a tumble.
Effective Practice Trading Techniques
Effective practice trading involves more than just randomly clicking buttons. A structured approach is key. Begin by focusing on understanding the fundamentals: chart patterns, technical indicators, and fundamental analysis. Then, develop a simple, well-defined trading strategy and stick to it. Avoid overcomplicating things, especially in the beginning.
Gradually increase the complexity of your trades as you gain confidence and experience. Regularly review your trades, analyze your mistakes, and adapt your strategy accordingly. This iterative process is essential for continuous improvement. Remember, consistency is more important than making huge profits in your demo account.
Common Mistakes Beginners Make
Many beginners fall into the trap of treating their demo account as a casino. They engage in reckless trading, neglecting risk management, and chasing quick profits. This leads to unrealistic expectations and ultimately, disappointment when they transition to live trading. Another common mistake is over-leveraging, taking on too much risk, and not sticking to a well-defined trading plan.
It’s crucial to understand that the forex market is not a get-rich-quick scheme. It demands patience, discipline, and a long-term perspective. Success requires consistent effort and continuous learning.
So you’ve mastered our comprehensive guide to FX spot trading for beginners, conquered the currency markets like a financial ninja, and are raking in the dough? Fantastic! But before you buy that private island, remember to check out this crucial guide: Understanding Canadian tax implications for forex trading profits to ensure your hard-earned profits aren’t swallowed by Uncle Sam…
err, the Canadian Revenue Agency. Then, get back to that beginner’s guide and refine your skills!
Setting Up and Using a Demo Account
The process of setting up a demo account is usually straightforward. Most reputable forex brokers offer demo accounts with a simple registration process. Typically, you’ll need to provide some basic personal information, and then you’ll be granted access to a virtual trading environment with a simulated amount of capital. The platform’s interface will be identical to the live trading platform, allowing you to practice using the same tools and features.
So you’re diving into our comprehensive guide to FX spot trading for beginners? Excellent! But hey, while you’re mastering the art of currency exchange, why not diversify your portfolio? Check out profit from cryptocoin to see if the volatile world of digital currencies tickles your fancy. Then, armed with both forex and crypto knowledge, you’ll be a financial ninja, ready to conquer any market!
Once you’re logged in, you can start placing trades, monitoring charts, and analyzing market data, all without risking any real money. Remember to choose a broker with a reputable history and a user-friendly platform. Don’t be afraid to explore different platforms to find one that suits your trading style.
Regulation and Security
Entering the wild world of FX spot trading is like stepping onto a rollercoaster – thrilling, potentially lucrative, but also requiring a hefty dose of caution. One crucial aspect often overlooked by beginners is the importance of regulation and security. Choosing the right broker isn’t just about finding the best platform; it’s about safeguarding your hard-earned money and ensuring a fair trading environment.The FX market, while exciting, is also a breeding ground for unscrupulous individuals.
So you’re diving headfirst into our comprehensive guide to FX spot trading for beginners? Fantastic! But before you risk your hard-earned cash, wise traders practice first. Check out this helpful resource to find the best app for paper trading: Which app is best for practicing paper trading before live trading? Then, armed with virtual victories (and hopefully few virtual defeats!), you’ll be ready to conquer the real FX market with our guide.
Understanding regulatory frameworks and implementing robust security measures is paramount to a successful and stress-free trading experience. Think of it as wearing your safety harness before taking that first plunge!
Key Regulatory Bodies Overseeing the FX Market
Numerous organizations worldwide oversee the FX market, ensuring brokers adhere to specific standards and protect investors. These bodies vary in their regulatory powers and the level of protection they offer. A broker’s regulation is a crucial indicator of its legitimacy and trustworthiness. The absence of regulation should be a major red flag.
- The Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) in the UK: Known for its stringent regulations and robust investor protection schemes.
- The Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) in the US: Oversees futures and options trading, including some aspects of the FX market.
- The Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC) in Australia: Another well-respected regulatory body with a focus on investor protection.
- The European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA) in Europe: Coordinates regulatory activities across the EU member states.
Risks Associated with Unregulated Brokers and Scams
Dealing with unregulated brokers is akin to walking a tightrope blindfolded. The absence of oversight leaves you vulnerable to a range of risks, including:
- Fraudulent Activities: Unregulated brokers can easily manipulate prices, engage in outright theft of funds, or disappear overnight with your investment.
- Lack of Investor Protection: In the event of disputes or broker insolvency, you have little to no recourse to recover your losses.
- Poor Execution Quality: Unregulated brokers might offer poor order execution, leading to slippage and increased trading costs.
- Cybersecurity Vulnerabilities: Unregulated entities often lack the robust security measures needed to protect your personal and financial information.
Security Measures to Protect Trading Accounts
Protecting your trading account from unauthorized access is critical. Think of your account as Fort Knox – you need multiple layers of security.Strong passwords, two-factor authentication (2FA), and regular software updates are essential first steps. Consider using a unique password for your trading account, different from other online accounts. 2FA adds an extra layer of security, requiring a code from your phone or another device to access your account, even if someone knows your password.
Keeping your trading software up-to-date is crucial to patching security vulnerabilities. Many brokers also offer additional security features like IP address restrictions, allowing you to limit access to your account only from specific devices or locations. Think of it as adding a moat around your Fort Knox!
The Importance of Choosing a Regulated Broker
Selecting a regulated broker is not merely advisable; it’s essential. Regulation provides a layer of protection, ensuring the broker adheres to specific standards of conduct and financial stability. This significantly reduces the risk of fraud and ensures a fairer trading environment. Choosing a regulated broker is akin to choosing a certified electrician rather than a handyman for wiring your house; you’re investing in peace of mind and security.
Fundamental Analysis in FX Trading
Forget crystal balls and tea leaves; fundamental analysis in FX trading is all about using real-world economic data to predict currency movements. It’s less about mystical hunches and more about understanding the economic forces that drive currency values. Think of it as being a financial detective, piecing together clues to solve the mystery of future exchange rates.Economic indicators are the bread and butter of fundamental analysis.
These are statistics released by governments and central banks that reflect the health of a nation’s economy. By analyzing these indicators, traders can gain insights into the potential future direction of a currency. A strong economy usually means a strong currency, while a struggling economy often leads to a weaker one. It’s not a perfect science, but it’s a powerful tool when used correctly.
The Role of Economic Indicators in FX Trading
GDP (Gross Domestic Product), inflation rates, and interest rates are three key players in the fundamental analysis game. GDP growth indicates the overall health of an economy; strong GDP growth typically boosts a currency’s value. Inflation, the rate at which prices rise, affects purchasing power and can influence interest rate decisions by central banks. High inflation usually puts downward pressure on a currency.
Interest rates, set by central banks, influence borrowing costs and investment flows. Higher interest rates generally attract foreign investment, strengthening the currency. These three indicators often work in concert, creating a complex interplay that seasoned traders carefully observe. For example, a country with strong GDP growth might see higher inflation, leading its central bank to raise interest rates to cool things down.
This could strengthen the currency initially, but if inflation remains stubbornly high, the currency might weaken in the long run.
Interpreting Economic News and its Impact on Currency Pairs
Imagine this: The US releases unexpectedly strong employment data. This positive news suggests a healthy US economy, potentially leading to higher interest rates. Traders might anticipate the dollar (USD) appreciating against other currencies, such as the euro (EUR), resulting in a potential rise in the EUR/USD exchange rate. Conversely, if a country announces unexpectedly weak economic data, like a sharp decline in manufacturing output, its currency is likely to weaken against other currencies.
The key is to understand the context of the news. A single data point rarely tells the whole story; traders need to consider the broader economic picture and how the news might affect future central bank decisions.
Using Fundamental Analysis to Identify Trading Opportunities
Let’s say you’re observing the GBP/USD (British pound/US dollar) pair. You notice that the UK’s inflation rate is significantly higher than the US inflation rate, and the Bank of England is expected to raise interest rates more aggressively than the Federal Reserve. This suggests that the GBP might appreciate against the USD. Fundamental analysis would support a long position (buying GBP/USD), anticipating the pair’s price to rise.
However, remember that unforeseen events can always impact the market, so thorough risk management is crucial. A sudden geopolitical event, for instance, could easily override the expected impact of these economic indicators.
Key Economic Indicators to Monitor
Understanding the interplay of various indicators is crucial. A single indicator in isolation rarely paints a complete picture.
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP): Measures the total value of goods and services produced in a country.
- Inflation Rate (CPI or PPI): Measures the rate at which prices for goods and services are increasing.
- Interest Rates: Set by central banks, influencing borrowing costs and investment flows.
- Unemployment Rate: Indicates the percentage of the labor force that is unemployed.
- Trade Balance: The difference between a country’s exports and imports.
- Consumer Confidence Index: Measures consumer sentiment regarding the economy.
- Manufacturing PMI (Purchasing Managers’ Index): An indicator of manufacturing activity.
Technical Analysis in FX Trading
Technical analysis is the art (and sometimes the science!) of predicting future price movements based on past market data. Forget crystal balls; we’re talking charts, graphs, and indicators – the tools of the technically-minded trader. It’s all about identifying patterns and trends to gain an edge in the often-chaotic world of forex. While fundamental analysis looks at the bigger picture (economic news, political events, etc.), technical analysis focuses on the price action itself.
Chart Types and Technical Indicators
Technical analysis relies heavily on charts to visualize price movements over time. The most common are bar charts, candlestick charts, and line charts. Each offers a slightly different perspective on price action. Bar charts show the high, low, open, and close prices for a given period. Candlestick charts provide the same information but in a more visually appealing and informative way, using “candles” to represent price ranges.
Line charts simply connect the closing prices, providing a smooth representation of the trend. Technical indicators, mathematical calculations based on price and volume data, are overlaid on these charts to help identify potential trading opportunities. Popular indicators include moving averages (smoothing out price fluctuations to reveal trends), relative strength index (RSI, measuring momentum), and MACD (measuring the relationship between two moving averages).
These indicators, when used correctly, can help traders identify potential entry and exit points, confirm trends, or spot potential reversals.
Chart Patterns
Recognizing chart patterns is a crucial skill for technical traders. These patterns, formed by price action over time, can predict future price movements. For example, a “head and shoulders” pattern, which looks like, well, a head and shoulders on the chart, often signals a potential trend reversal. The “head” represents a peak in price, followed by two smaller “shoulders,” indicating weakening momentum.
A “double top” or “double bottom” pattern suggests a potential trend reversal as well. A double top occurs when the price reaches a peak twice, failing to break through resistance, while a double bottom shows the opposite – two lows with the price failing to break support. These patterns, while not foolproof, provide strong indications of potential price movements and should be considered alongside other technical indicators.
Candlestick Patterns
Candlestick charts are incredibly useful in technical analysis due to their visual nature. Each candle provides a wealth of information, showing the open, high, low, and close prices. Specific candlestick patterns can signal potential price movements. For example, a “hammer” candlestick, characterized by a long lower wick (the line extending below the body of the candle) and a small body, often indicates a potential bullish reversal.
Conversely, a “hanging man” pattern, similar to a hammer but occurring at the top of an uptrend, suggests a potential bearish reversal. Doji candles, which have almost equal open and close prices, indicate indecision in the market, potentially signaling a change in trend. The interpretation of candlestick patterns often depends on their context within the overall chart pattern and trend.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Using Technical Analysis
1. Choose your chart
Select a chart type (bar, candlestick, line) that suits your trading style and preferences.
2. Select your timeframe
Determine the timeframe you will be trading on (e.g., 15-minute, daily, weekly charts). The timeframe you choose dictates the type of trades you will take (scalping, day trading, swing trading).
3. Identify trends
Use moving averages or other indicators to determine the overall trend (uptrend, downtrend, or sideways).
4. Identify support and resistance levels
These are price levels where the price has historically struggled to break through. Support levels are price floors, while resistance levels are price ceilings.
5. Look for chart patterns
Identify any potential chart patterns (head and shoulders, double tops/bottoms, etc.) that might suggest future price movements.
6. Use technical indicators
Employ indicators such as RSI, MACD, or stochastic oscillators to confirm trends or potential reversals.
7. Develop a trading plan
Based on your analysis, develop a clear trading plan outlining entry and exit points, stop-loss orders, and take-profit levels.
8. Manage risk
Always use appropriate risk management techniques to protect your capital. Never risk more than you can afford to lose.
Illustrative Examples of Successful and Unsuccessful Trades

Let’s ditch the boring textbook examples and dive into some real-world FX trading scenarios – the triumphs and the (let’s be honest) epic fails. Understanding both sides of the coin is crucial for becoming a savvy trader. We’ll examine the strategies, the market conditions, and the crucial decisions that led to both success and… well, let’s just say “opportunities for growth.”Successful trades aren’t just about luck; they’re about meticulous planning and a healthy dose of discipline.
Unsuccessful trades, on the other hand, are fantastic learning experiences, provided you’re willing to analyze what went wrong.
Successful Trade: EUR/USD Long Position
This trade capitalized on a weakening US dollar against the Euro. The trader, let’s call him “Bob,” identified a period of low volatility followed by a clear upward trend in the EUR/USD pair. Bob’s analysis, using a combination of fundamental (positive Eurozone economic data) and technical indicators (a bullish crossover of the 50- and 200-day moving averages), suggested a strong probability of the Euro appreciating against the dollar.
He opened a long position at 1.1000. Over the next two weeks, the EUR/USD pair steadily rose, reaching 1.1250. Bob closed his position, realizing a profit of 250 pips (1 pip = 0.0001). A chart illustrating this would show a gradual upward sloping line from 1.1000 to 1.1250 over a two-week period. The chart would also include the moving average lines clearly showing the bullish crossover before the price increase began.
Unsuccessful Trade: GBP/JPY Short Position
“Alice,” our intrepid trader, entered a short position in GBP/JPY based solely on a hunch. She saw a recent peak in the pair and assumed a correction was imminent. She didn’t conduct any thorough fundamental or technical analysis; she just felt it was time to sell. The GBP/JPY pair, however, defied her expectations and continued its upward trajectory.
Alice held onto her losing position, hoping for a reversal, but the price kept climbing. Eventually, she was forced to close her position at a significant loss, having failed to set a stop-loss order. A chart of this trade would show a sharp upward trend, completely opposite to Alice’s prediction. The absence of a stop-loss order would be visually represented by the continued upward trend, extending beyond the point where a stop-loss would have minimized her losses.
The chart would highlight the significant gap between her entry price and the exit price, showcasing the magnitude of her loss.
Successful Trade: USD/JPY Scalping
“Charlie,” a skilled scalper, used a fast-paced trading strategy to capitalize on short-term price fluctuations. Observing a period of high volatility in the USD/JPY pair, Charlie identified a minor price dip using a combination of candlestick patterns and short-term moving averages. He opened a long position, expecting a quick rebound. Within minutes, the price rallied as predicted, and Charlie closed his position for a small but quick profit.
The chart would show a very sharp V-shaped price movement, illustrating the rapid increase after the dip. This demonstrates the effectiveness of his strategy in capitalizing on short-term price swings. The chart would also likely show a confluence of technical indicators confirming his entry and exit points.
Unsuccessful Trade: Ignoring Stop-Loss Orders
This example doesn’t focus on a specific currency pair but on a common mistake: ignoring stop-loss orders. A trader, let’s call him “David,” entered a long position in EUR/USD with a target profit of 100 pips. However, he failed to set a stop-loss order. When the market moved against him, his losses mounted significantly. The absence of a stop-loss order allowed the losses to snowball.
The chart would illustrate a gradual decline in price, with the loss increasing steadily without any limit until the trader was forced to close the position manually. This demonstrates the crucial role of stop-loss orders in risk management. The visual representation would highlight the potentially unlimited loss, contrasting it with the limited potential profit.
Last Recap: Comprehensive Guide To FX Spot Trading For Beginners
So, you’ve journeyed through the labyrinthine world of FX spot trading, armed with knowledge and (hopefully) a healthy dose of caution. Remember, the FX market is a beast of unpredictable beauty; respect its power, understand its whims, and always, always, have a solid risk management plan in place. This isn’t a get-rich-quick scheme, but with dedication, practice, and a dash of luck, you might just find yourself laughing all the way to the bank (or, at least, to a slightly more comfortable financial situation).
Happy trading!
